The Far East is the eastern part of Asia. He understands :
- East Asia (Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, China, etc.). For Japan, see Shinto
- Southeast Asia (Malaysia, Burma, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Indonesia, etc.)
- the Russian Far East, in particular the Pacific provinces and their hinterland.
Much of the Far East was influenced by the various Empires of China. Our list also includes the Oceania region.

Contents
ToggleFestivals in the Far East and Oceania
Holidays of the month
July 7, 2025 (1 event)
July 7, 2025

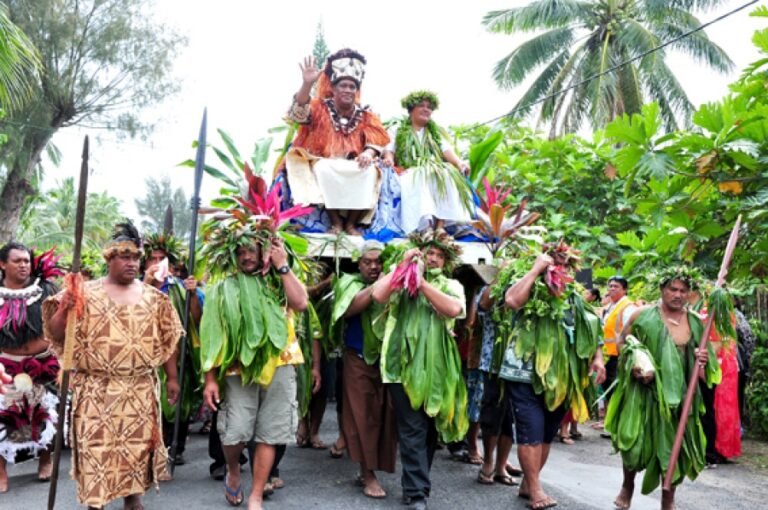
Today in the Cook Islands takes place Ra o te Ui Ariki. This day celebrates the Ariki, the chiefs of the various Vaka of the islands. This is an opportunity to honor the different local cultures and customs. #mythology #myth #legend #calendar #vaka #Ariki
July 11, 2025 (2 events)
July 11, 2025

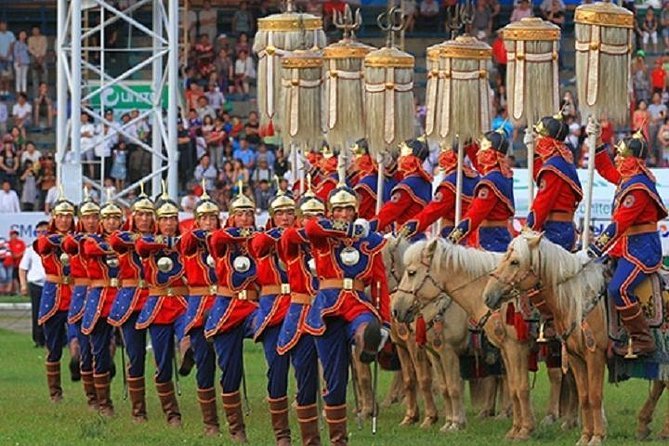
Today, the peoples of Mongolia celebrate Naadam. During this festival, a competition of archery, wrestling and equestrian sports is disputed between the best athletes of each people. #mythology #myth #legend #calendar #July 11 #mongolia #Naadam
–
July 11, 2025
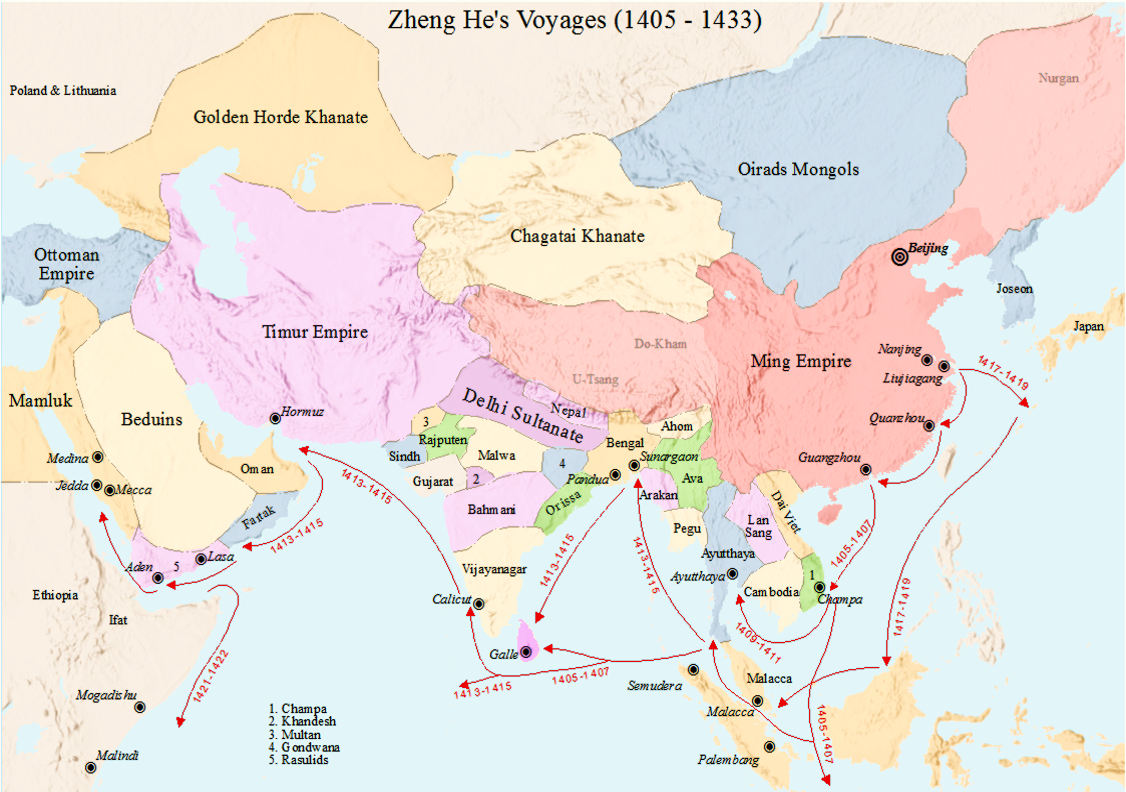
Today, the Chinese commemorate Zheng He's first voyage on July 11, 1405 with 317 boats. During these seven expeditions, he mapped, put in contact with and traded with all the coasts south of Liuj iagang, up to present-day Indonesia and Somalia. #mythology #myth #legend #calendar #ZhengHe #July 11 #Chine #Ming
Cultural areas in the Far East and Oceania
East Asia (or Eastern Asia) is a region of Asia, including: China, Korea (North Korea and South Korea), Japan, Mongolia (sometimes attached to Central Asia) , Taiwan, possibly Vietnam and Singapore, for cultural reasons (these countries are more generally attached to Southeast Asia for their geographical position), the Russian Far East can also be attached to this region.
China was the first colonized region in East Asia and was undoubtedly the core of East Asian civilization from which the other parts of East Asia formed. The various other regions of East Asia have been selective in the Chinese influences they have adopted into their local customs.
The religious phenomenon in the Chinese world is characterized by pluralism, favored by the attitude of the State: since the beginning of the empire (3rd century BCE), the latter has exercised careful control over groups likely to constitute a threat. for power and society and brings overly active sects into line, only exceptionally granting exclusivity to a cult. Syncretism and mixing are common, making the contours of religious groups blurred; we have the impression of being faced with a constellation of philosophies and practices rather than confessions.
Taoism, or rather the Taoist currents, appeared from the 2nd century, inspired by the currents of Yin and Yang and the Five Elements, as well as by the writings of the philosopher Lao Tseu (or Lao-tseu) (老子) dating from the mid-first millennium BC BC, including the famous Book of the Way and Virtue (Tao Tö King), is, with the Book of Changes (Yi Jing), at the sources of Chinese esotericism. These currents were constantly enriched with new influences and provided the whole of Chinese religion with many of its concepts and practices as well as a number of deities.
Founded on the teaching of the life of Confucius, notably through his Analects and the works of his disciples such as Mencius, Confucianism (rujiao 儒教) was established as a state doctrine, reaching its peak during the Song dynasty. Naturally devoted to the interpretations of the ruling dynasties, the original doctrine of Confucius is however not necessarily synonymous with submission to institutions, as some contemporaries observe. Historically, however, Confucianism helped to impose the ideology of the “five relationships” between subjects, intended to strengthen social order and the cosmic link between hierarchical position and celestial virtue.